Research Project Website
Privacy Risks in Data Collection and Storage
As businesses collect more personal information to improve services and tailor experiences, there are growing concerns about the safety and privacy of that data. This information can include things like names, addresses, payment details, browsing habits, and even health data. While this helps businesses provide better services, the risk of misusing this data becomes higher as it grows in size and sensitivity.
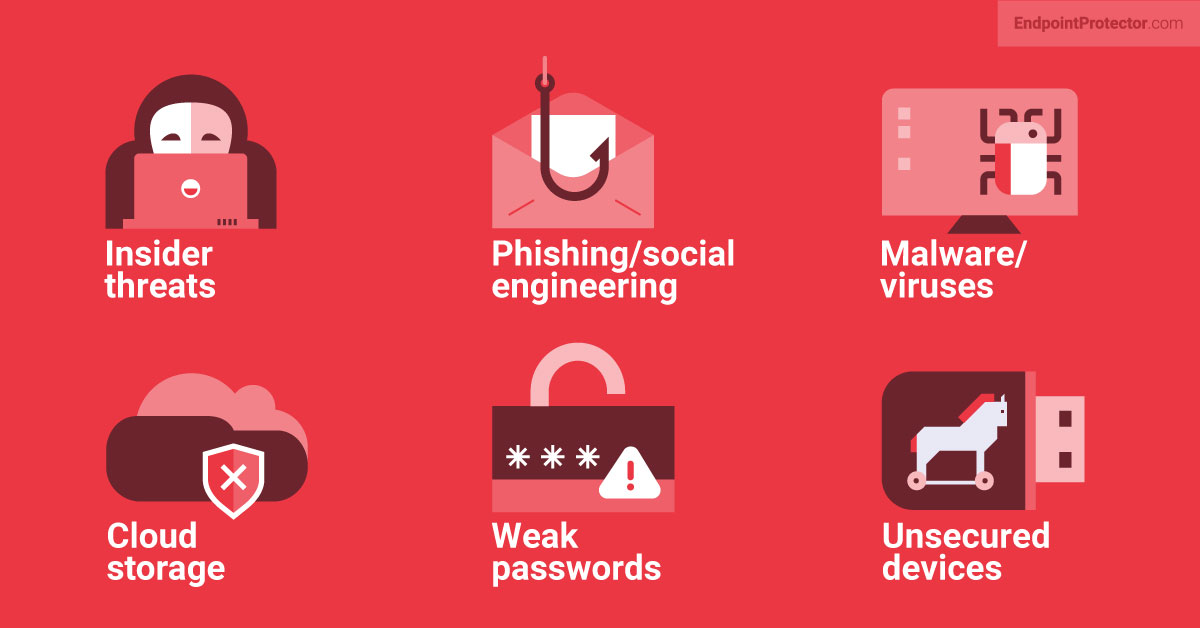
One main problem is that people often don’t fully understand how their data is being collected, stored, or shared. Sometimes, businesses collect too much information without clearly asking for consent or explaining how it will be used. As technologies like AI and tracking cookies become more common, people may end up sharing personal data across multiple websites without realizing it, which increases the chances of their data being misused.
Another issue is how this data is stored. Big databases with sensitive personal information are prime targets for hackers. Even with encryption, if security isn’t implemented properly—like weak passwords or outdated software—cybercriminals can find ways to get in and cause a breach. When this happens, it can lead to financial losses for businesses and make customers lose trust in the company.
A well-known example of this is the Equifax breach in 2017. The personal data of over 147 million Americans was exposed because Equifax didn’t fix vulnerabilities in their system in time. Sensitive details like social security numbers and birth dates were exposed, making victims more likely to face identity theft or fraud. This incident showed just how important it is for businesses to keep security measures up to date and protect sensitive customer information.
Misuse of Computing Resources
Misuse of computing resources refers to scenarios where attackers exploit vulnerabilities or hijack computing power for malicious purposes. As digital infrastructures evolve, these resources become increasingly valuable, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. One of the most common and damaging forms of misuse is cryptojacking, a type of cyberattack where hackers covertly use a victim’s computing resources to mine cryptocurrency. In these attacks, the victim’s CPU or GPU is hijacked without consent, often causing performance degradation, slower system speeds, and an increase in electricity consumption. For businesses, cryptojacking can result in higher operating costs and even complete system failure if the attack goes unnoticed for too long.
Another form of misuse is the creation of botnets. These are networks of compromised computers or devices that are controlled remotely by attackers. A well-known example of this is the Mirai Botnet, which was responsible for one of the largest Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks in history. The Mirai Botnet infected thousands of Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as cameras and routers, using them to flood targeted websites with malicious traffic, rendering them inaccessible. These attacks exploited weak or poorly configured IoT devices, highlighting how the rapid growth of the IoT ecosystem has created new attack surfaces for hackers.
To combat the misuse of resources, businesses must implement robust cybersecurity defenses. This includes deploying firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular software updates. It’s also essential to monitor for unusual network activity that could indicate misuse of computing resources. Additionally, businesses should educate employees and end users on recognizing and avoiding potential vulnerabilities, such as falling victim to phishing schemes or using unsecured IoT devices.
Unauthorized Access to Information
Unauthorized access occurs when malicious actors or even insiders gain access to data or systems they are not authorized to use. The consequences of such breaches can be severe, ranging from financial loss to reputational damage, depending on the sensitivity of the information involved. Hackers use various techniques to gain unauthorized access, including phishing, brute-force attacks, and exploiting vulnerabilities in software or hardware.
Phishing remains one of the most common methods of unauthorized access. This technique involves sending fraudulent emails or messages that appear to come from legitimate sources, such as banks or service providers. These messages often prompt users to click on links or download attachments, which then steal their login credentials or install malware on their systems. Since phishing attacks often look convincing, they can be particularly difficult to spot, especially for individuals who are not tech-savvy.
Another frequent method of unauthorized access is brute-force attacks, where an attacker uses automated software to repeatedly guess passwords until the correct one is found. Many people use weak or reused passwords across multiple accounts, which makes these types of attacks more successful. With the growing number of data breaches, attackers can sometimes obtain vast collections of compromised passwords from previous leaks, which can be used to target users across different platforms.
To mitigate the risk of unauthorized access, companies should adopt several layers of defense, including encryption of sensitive data, which ensures that even if attackers gain access to the data, they cannot read it without the proper decryption keys. Another essential practice is implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), which adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through more than just a password—such as using a one-time code sent to their phone. Access controls should also be established to restrict system access to only those who need it and ensure that users only have access to the information they are authorized to view.
The Yahoo Data Breach in 2013 serves as a reminder of how unauthorized access can affect millions of people. The breach compromised over 3 billion accounts, exposing personal information such as email addresses, phone numbers, and security questions. The hackers behind this breach gained access to Yahoo’s systems through a combination of weak security measures and compromised passwords, leading to one of the largest data breaches in history.
Risks Associated with Computing Innovations
Technological innovations like artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and blockchain have significantly transformed industries, offering new solutions to old problems and enhancing operational efficiency. However, these innovations come with their own set of risks and ethical concerns.
AI has revolutionized fields like healthcare, where it is used for diagnostic tools that help detect diseases faster and more accurately than human doctors in some cases. AI is also used for personalized recommendations in various industries, such as e-commerce and entertainment. However, AI systems can also unintentionally perpetuate biases if they are trained on biased data sets. For example, if an AI algorithm used for hiring decisions is trained on data that reflects historical inequalities, it may inadvertently discriminate against certain demographic groups, reinforcing existing societal biases. The growing use of AI raises questions about accountability, transparency, and fairness, especially when decisions made by AI systems impact people's lives.
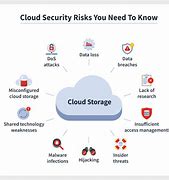
Cloud computing has provided businesses with the ability to store, access, and process data remotely, increasing scalability and reducing costs. However, the widespread adoption of cloud services has introduced new privacy concerns. Sensitive data stored off-site, often across multiple locations or with third-party providers, can be exposed if cloud providers do not implement proper security measures. The lack of direct control over cloud infrastructure means that businesses must rely heavily on their service providers to maintain robust security.
Blockchain technology, while known for its role in cryptocurrencies, has also found applications in various sectors such as finance, supply chain management, and voting systems due to its ability to provide secure, transparent, and immutable records. However, blockchain’s anonymity can be exploited for illicit activities, such as money laundering and dark web transactions. Moreover, the technology’s environmental impact—especially with energy-intensive cryptocurrency mining—has raised concerns about sustainability.
Despite these risks, computing innovations have the potential to create immense societal value, and it's crucial to balance the benefits with appropriate safeguards. Companies and policymakers need to address the ethical and security challenges posed by these technologies to ensure they are used responsibly and equitably.